
They have been shown to originate from small brain regions. 1999 52:1-304.High frequency oscillations (HFOs) are emerging as biomarkers of epileptogenicity. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl. Recommendations for the Practice of Clinical Neurophysiology: Guidelines of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Evaluation of the first seizure in adults. Philadelphia: Butterworth-Heinemann 2000. Neurology in Clinical Practice (3rd edition). Bradley WG, Daroff RB, Marsden CD, et al (eds).Vrocher D, Lowell MJ, Plantz SH. Electroencephalography (EEG).
#No eeg download#
Hence the doctor will almost always recommend this test when it is needed.Īssociate Professor Karl Ng MB BS (Hons I) FRCP FRACP PhD CCT Clinical Neurophysiology (UK) Consultant Neurologist – Sydney North Neurology and Neurophysiology ( download referral form and map) Conjoint Associate Professor – Sydney Medical School, University of Sydney and Editorial Advisory Board Member of the Virtual Neuro Centre. This test is usually totally non-invasive and has very few side effects apart from potential seizure activities during the procedure.
It must be remembered that EEG does not provide stimulation to the brain – it merely detects and receives electrical signals from the brain. While not particularly uncomfortable (sometimes accompanied by dizziness), an abnormality on the EEG is what is desired during the procedure. To provoke abnormalities in the EEG, the patient may be asked to do certain activities such as deep breathing.
However, most patients will not be told to stop their medication for seizures. Occasionally and sometimes because a patient may be withheld from antiepileptic medications or had medications reduced, the patient may experience clinical seizures during the procedure. The results will be discussed with the patient by the doctor or referring clinician.Īn EEG is a non-invasive procedure, hence very few risks are associated with it. If the patient has a high possibility of having a seizure, someone should take care of the patient. After the test, the patient is usually allowed to go home without the need for a recovery period provided the test went smoothly. If an ambulatory EEG is done, it typically lasts for 24 hours, but the patient is allowed to perform daily activities. If a sleep EEG is performed, it may last for 2-3 hours.
#No eeg series#
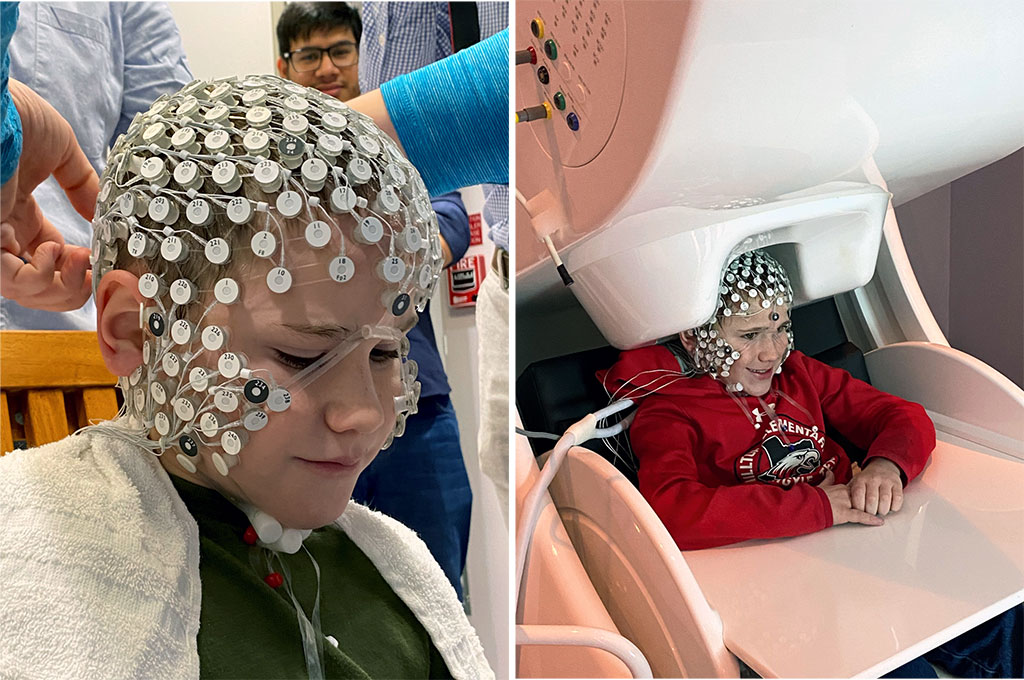
Additionally, there may also be a series of flashes given with a light strobe. The technician/nurse/doctor might ask the patient to breathe deeply for many times in a short period to provoke or enhance any abnormalities on the EEG. After that, 16-20 electrodes will be attached to the scalp by using gel. The patient will be positioned on a bed or chair.

Hair styling products (hairspray or gel) should be avoided during the day of test as this impedes electrode placement on the scalp.At least 8 hours before the test, foods that contain caffeine (coffee, tea, cola, chocolate) should be avoided.These can affect the test but it is very important that you consult your doctor before you stop them. These can include sedatives, tranquilisers, sleeping tablets and medications for epilepsy. Before the day of EEG, medications that can affect brain activity may be ceased, but this is not usually necessary.After that, the doctor or laboratory will advise the patients of the following: It remains an important adjunct in the detection of temporal lobe involvement in encephalitis, for example due to herpes infection.īefore the test, a complete medical history will be taken by the doctor ordering the test to determine if the EEG is really necessary and indicated. Much less frequently nowadays, to localise suspected lesions of the brain such as tumour, inflammation, infection, or vascular events like stroke.To monitor brain activity when a person is under general anaesthesia.To evaluate cognitive impairment and dementia.The assessment of impaired consciousness or altered mental state.The test can help classify the type of epilepsy and also differentiate it from non-epileptic events. However a normal EEG does not exclude the diagnosis of epilepsy. As an aid to the diagnosis of epilepsy: This is the most useful and important test in confirming a diagnosis of epilepsy.They are picked up by the electrodes on the surface of the scalp, and therefore the standard test may not be able to show smaller activity that occurs deep within the brain.Īn EEG is done for the following reasons: The waveforms in the EEG are generated by impulses near the communication between neurons or nerves in the brain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
